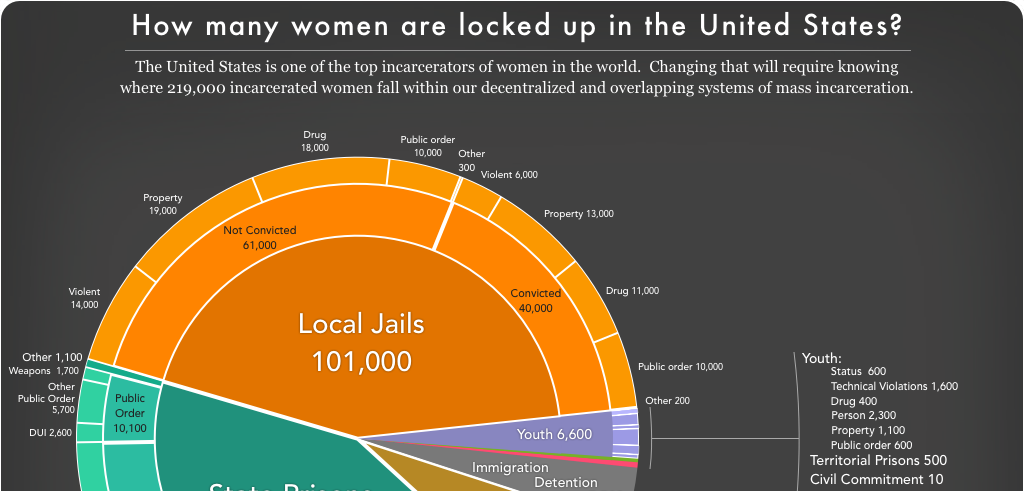
New report, Women’s Mass Incarceration: The Whole Pie 2019, reveals how many women are locked up in the U.S., where, and why
The report highlights the need for reforms to local jails, which now hold more women than state prisons do.
October 29, 2019
A report released this morning by the Prison Policy Initiative and the ACLU Campaign for Smart Justice presents the most recent and comprehensive data on how many women are locked up in the U.S., where, and why.
Women in the U.S. experience a dramatically different criminal justice system than men do, but data on their experiences is difficult to find and put into context. The new edition of Women’s Mass Incarceration: The Whole Pie, which the Prison Policy Initiative and ACLU have published every year since 2017, fills this gap with four richly-annotated data visualizations about women behind bars.
“Producing this big-picture view of incarcerated women helps us see why many recent criminal justice reforms are failing to reduce women’s incarceration,” said report author Aleks Kajstura. Most importantly, the new report underscores the need for reforms to local jails:
- More incarcerated women are held in local jails than in state prisons, in stark contrast to incarcerated men, meaning that reforms that only impact people in prison will not benefit them.
- The number of women in local jails grew between 2016 and 2017 — a trend that reflects counties’ growing reliance on jails to solve social problems.
- Women convicted of criminal offenses are more likely than men to be serving their sentences in local jails, where healthcare and rehabilitative programs are much harder to access than in prisons.
- On any given night, 4,500 immigrant women are held for ICE in local jails — over half of the 7,700 women held in immigration detention.
The report goes on to explain why 231,000 women are locked up in the U.S.:
- 73% of women in prisons and jails are locked up for nonviolent offenses, in contrast to only 57% of all people in prisons and jails (who are almost entirely men).
- 10% of girls in the juvenile justice system — compared to only 3% of boys — are held for status offenses like running away, truancy, or “incorrigibility,” which would not be crimes if committed by adults.
- 27% of women in prisons and jails are locked up for violent offenses, including acts of violence committed in self-defense.
Beyond presenting new data, Women’s Mass Incarceration: The Whole Pie 2019 also reviews the existing literature on women’s incarceration, including the Prison Policy Initiative’s prior research on gender disparities in police contact, women’s access to reentry services after incarceration, and the incomes of women in prisons and jails.