New data reveals where people in Maryland prisons come from
Report shows every community is harmed by mass incarceration
June 27, 2022
Today the Prison Policy Initiative and Justice Policy Institute released a new report, Where people in prison come from: The geography of mass incarceration in Maryland, that gives an in-depth look at where people in Maryland state prisons come from. The report also provides 9 detailed data tables — including neighborhood-specific data for Baltimore City and Montgomery County — that serve as a foundation for advocates, organizers, policymakers, data journalists, academics, and others to do their own analysis of how incarceration relates to other factors of community well-being.
The report shows:
- Every single county — and every legislative district — is missing a portion of its population to incarceration in state prison;
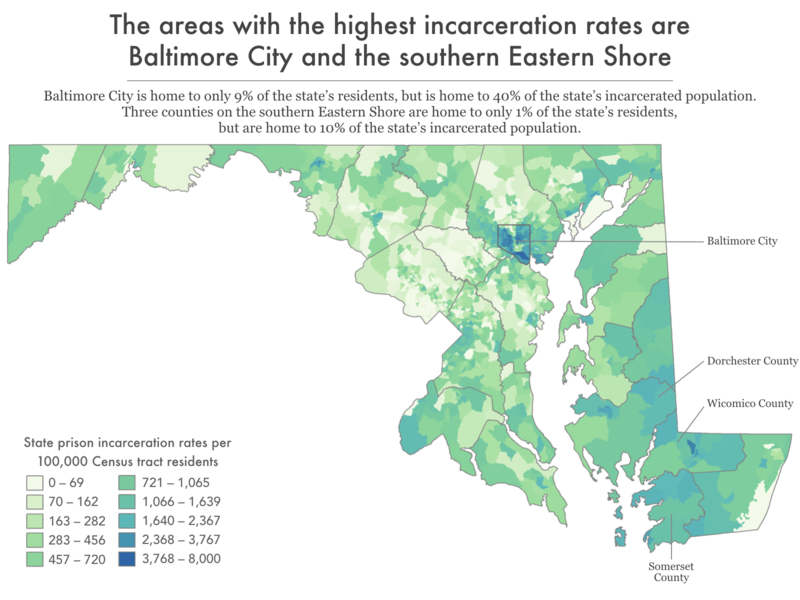
- No city is harmed by mass incarceration as much as the city of Baltimore. It is home to 9% of the state’s residents, but 40% of people in its state prisons.
- Smaller and traditionally under-resourced Eastern Shore communities are particularly hard hit by mass incarceration; and
- The worst impacts of mass incarceration are often concentrated in specific neighborhoods that are already systematically under-resourced. For example, over a third of the people from the city of Baltimore in state prison come from just 10 of the cities 55 neighborhoods.
Data tables included in the report provide residence information for people in Maryland state prisons at the time of the 2020 Census, offering the clearest look ever at which communities are most impacted by mass incarceration. They break down the number of people locked up by county, city, town, zip code, legislative district, census tract, and other areas.
The data show the counties with the highest state prison incarceration rates are Wicomico, Dorchester, and Somerset, all with incarceration rates greater than 500 people in state prison per 100,000 residents. For comparison, Montgomery County has the lowest prison incarceration rate, at 61 people in state prison per 100,000 residents, roughly 10 times lower than the highest counties.
“The nation’s 40-year failed experiment with mass incarceration harms each and every one of us. This analysis shows that while some communities are disproportionately impacted by this failed policy, nobody escapes the damage it causes,” said Emily Widra, Senior Research Analyst at the Prison Policy Initiative. “Our report is just the beginning. We’re making this data available so others can further examine how geographic incarceration trends correlate with other problems communities face.”
A previous analysis from the Prison Policy Initiative and Justice Policy Institute showed a strong correlation between high rates of incarceration in Maryland and high unemployment rates, long commute times, low household incomes, decreased life expectancy, and other markers of low community well-being.
The data and report are made possible by the state’s landmark 2010 law that requires that people in prison be counted as residents of their hometown rather than in prison cells when state and local governments redistrict every ten years. Maryland was the first state in the nation to end the practice of “prison gerrymandering,” which gave disproportional political clout to state and local districts that contain prisons at the expense of all of the other areas of the state. Since then, more than a dozen states and 200 local governments have taken steps to end the practices. In total, roughly half the country now lives in a place that has taken action to address prison gerrymandering.